Evaluation of power sources and the effect of varying current in SMAW process

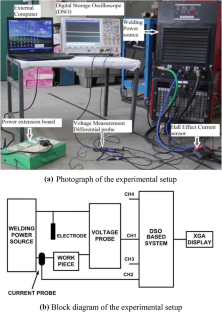
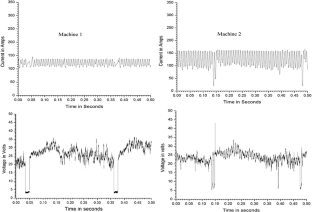
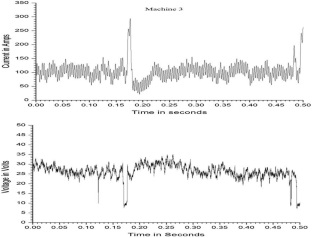
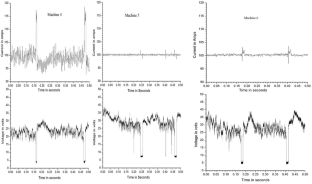
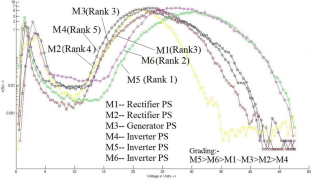
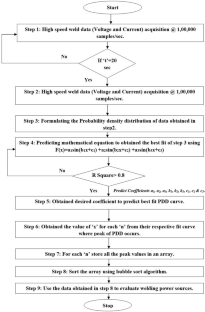
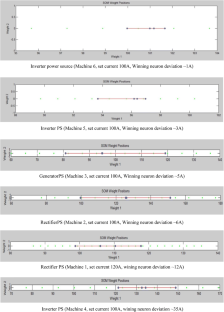
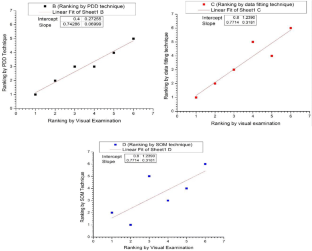
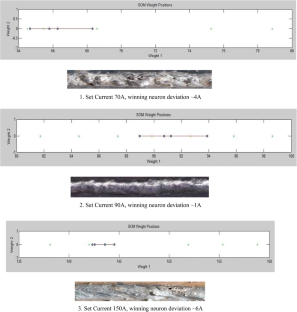
Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) is one of the most important welding process used in the industry for joining ferrous and nonferrous metals. In SMAW process random fluctuations in current and voltage takes place. Reliable acquisition of these variations during actual welding process and its subsequent analysis can be very useful to study different arc welding parameters. Now a day, the welding power sources have a provision of advance arc control to suitably adjust the welding parameters with minimum time delay and to set the right welding parameters during actual process. Hence, to study the exact behaviour of these modern power sources used for welding it is essential to acquire all the possible minute variations taking place while welding is in progress. In the present study, performance evaluation of six different welding power sources has been performed using probability density distributions (PDD) and self organized maps (SOM). Further the quantification of their performance has also been attempted and the final results were compared with the results obtained using existing techniques. The effect of varying input current on SMAW process has also been studied by acquiring the data at different current values (from 70 A to 120 A). In both the cases data acquisition was carried out at the rate of 100,000 samples/s for 20 s duration using a general purpose digital storage oscilloscope while welding is in progress. These welds were prepared using same type of welding electrode by the same welder employing the identical parameters. From the PDDs and self organized maps (SOM) generated using the data acquired, it is possible to evaluate the performances of the different welding power sources. Grading of the power sources based on PDD and SOM technique matched well with the grading obtained using visual examination of weld beads. Further using these analyses, it is also possible to differentiate various weld geometry. Results clearly indicated that the procedure presented here can be effectively used to assess the various SMAW parameters.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
Springer+ Basic
€32.70 /Month
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Buy Now
Price includes VAT (France)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve

Similar content being viewed by others
Performance Evaluation of Arc Welding Process Using Weld Data Analysis
Article 15 November 2018

Optimization methodology of alternating current P-GMAW process by voltage-current signal analysis
Article 17 December 2015
Qualitative and quantitative analyses of arc characteristics in SMAW
Article 21 January 2016
Explore related subjects
References
- Bing X (2011) Welding arc signal acquisition and analysis system based on VC++ and MATLAB mixed programming. In: IEEE proceedings 3rd third international conference on measuring technology and mechatronics automation (ICMTMA), vol. 3, pp 1150–1153
- Chen B, Han F, Huang Y, Lu K, Liu Y, Li L (2009) Influence of nanoscale marble (calcium carbonate CaCO3) on properties of D600R surfacing electrode. Weld. J. 88:99–103 Google Scholar
- Li X, Simpson SW (2009) Parametric approach to positional fault detection in short arc welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 14:146–151 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Mehotra K, Mohan CK, Ranka S (1997) Elements of artificial neural networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 187–202 Google Scholar
- Pal S, Pal SK, Samantaray AK (2008) Neurowavelet packet analysis based on current signature for weld joint strength prediction in pulsed metal inert gas welding process. Sci Technol Weld Join 13:638–645 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Pal S, Pal SK, Samantray AK (2010) Prediction of the quality of pulsed metal inert gas welding using statistical parameters of arc signals in artificial neural network. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 23:456–465 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Ramirez JE, Johnson M (2010) Effect of welding parameters and electrode condition on alloying enrichment of weld metal deposited with coated cellulosic electrodes. Weld J 89:232–242 Google Scholar
- Rehfeldt D, Polite T (1998) Systems for processing monitoring and quality assurance in welding. In: Proceedings of 8th international conference on computer technology in welding, American Welding Society, Miami
- Rehfeldt D, Rehfeldt M (2003) Computer-aided quality assurance (CAQ) of Al-GMAW-welding with Analysator Hannover. In: Proceedings international forum on automobile welding, Mechanical Engineering Press, Beijing
- Santhakumari A, Raja N, Rajasekaran P, Venkateswaran R (2014) Evaluation of welding power sourced and fillers wires through signature analysis. Welding Research Institute. National Welding Seminar, Jamshedpur
- Simpson SW (2007a) Signature image for arc welding fault detection. Sci Technol Weld Join 12:481–486 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Simpson SW (2007b) Statistics of signature images for arc welding fault detection. Sci Technol Weld Join 12:556–563 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Simpson SW (2008a) Fault identification in gas metal arc welding with signature images. Sci Technol Weld Joining 13:87–96 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Simpson SW (2008b) Signature image stability and metal transfer in gas metal arc welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 13:176–183 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Vikas K, Chandrasekhar N, Albert SK, Jayapandian J (2016a) Analysis of arc welding process using digital storage oscilloscope. Measurement 81:1–12 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Vikas K, Albert SK, Chandrasekhar N, Jayapandian J (2016b) Performance analysis of arc welding parameters using self-organizing maps and probability density distributions. In: IEEE first international conference on control, measurement and instrumentation, Kolkata, pp 196–200
- Vikas K, Albert SK, Chandrasekhar N, Jayapandian J (2018a) Evaluation of welding skill using probability density distributions and neural network analysis. Measurement 116:114–121 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Vikas K, Albert SK, Chandrasekhar N (2018b) Signal processing approach on weld data for evaluation of arc welding electrodes using probability density distributions. Measurement 113:23–32 Google Scholar
- Wu CS, Polte T, Rehfeldt D (2000) Gas metal arc welding process monitoring and quality evaluation using neural networks. Sci Technol Weld Join 5(5):324–328 ArticleGoogle Scholar
- Wu CS, Polte T, Rehfeldt D (2001) A fuzzy logic system for process monitoring and quality evaluation in GMAW. Weld J 80(2):16–22 Google Scholar
- Wu CS, Hu QX, Sun S, Polte T, Rehfeldt D (2004) Intelligent monitoring and recognition of the short-circuiting gas–metal arc welding process. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 218:1145–1151 ArticleGoogle Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- School of Electronics Engineering, Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, Deemed to be University, Bhubaneswar, 751024, Odisha, India Vikas Kumar & Manoj Kumar Parida
- Department of Instrumentation and Control Engineering, Dr. B R Ambedkar National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar, 144011, India O. P. Verma
- Vikas Kumar













